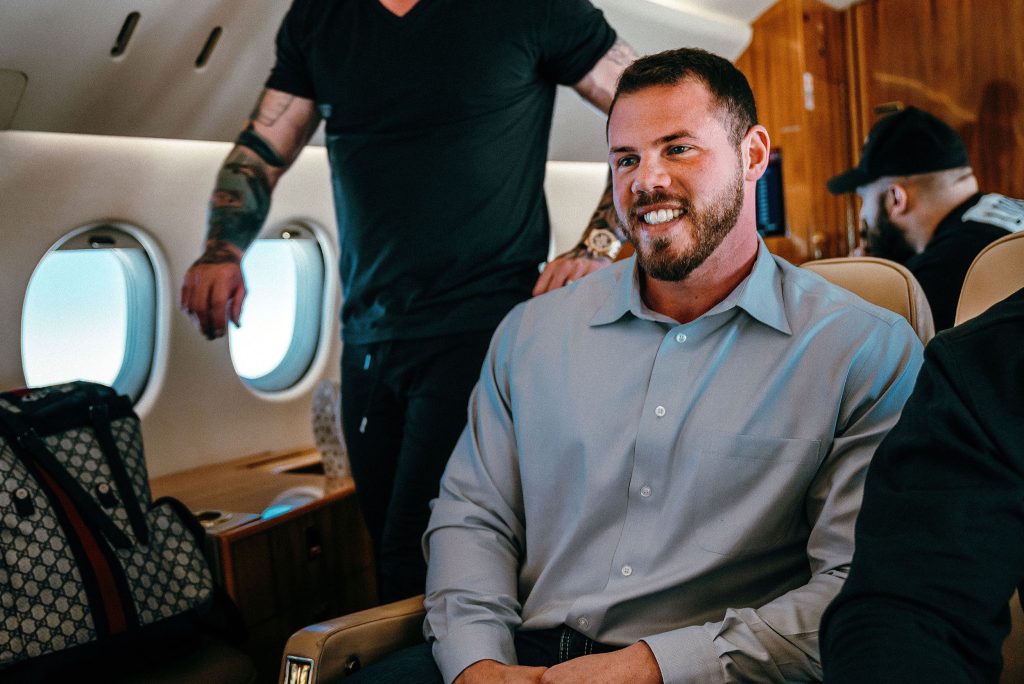
Nothing is Out of Reach
We understand your frustration. Scrolling through endless posts of self-proclaimed “gurus” preaching their overnight success tips can be disheartening, especially when you know that building & managing wealth takes a lot more than just one secret tip.
You’re not alone in feeling this way. It can be challenging to trust anyone these days, let alone those claiming to have the magic formula to instant riches. But we know what it takes to build a successful businesses, make sound investments and leverage next-generation technology because we’ve done it ourselves.
Here’s the truth: most of the gurus are wrong. Leveling up isn’t easy, but it’s not impossible either. What if you had access to a proven roadmap taught to you by people who have already traveled the path ahead of you? That’s where the Beyond Broke Mastermind comes in.
We’ve brought together a community of real entrepreneurs, investors, thought leaders and business owners who share their struggles and support each other through every aspect of life. We’ve created a family of extraordinary people who have each other’s backs, and we’re just getting started.
Imagine having access to a network of qualified individuals who you can turn to for advice when you need it most. That’s what the Beyond Broke Mastermind offers, and we invite you to join us on this journey towards success.

Collaboration
We understand the importance of having a supportive community when striving for excellence. While we believe in the power of the individual, we also know that it's better to enhance your efforts through collaboration.
History has shown us that the most successful empires were built on the foundation of individuals working together towards a common goal. That's why we've created a network of outliers and overachievers who are dedicated to helping each other reach their full potential.
By joining, you'll be part of a community that values collaboration and support.
Networking
One of the most valuable aspects of any organization is the connects you can make and the Beyond Broke Mastermmind is no exception. Meet other leaders and expand your network.

Scale & Expand
We're focused on helping ambitious entrepreneurs scale their businesses and wealth to 7, 8, and even 9 figures.
We're looking for individuals who have a burning desire to create something truly extraordinary. Our community is made up of empire-builders who are committed to achieving their goals and making a significant impact in the world.
We're focused on helping ambitious entrepreneurs scale their businesses and wealth to 7, 8, and even 9 figures.
We're looking for individuals who have a burning desire to create something truly extraordinary. Our community is made up of empire-builders who are committed to achieving their goals and making a significant impact in the world.
Jake Claver is a business leader, keynote speaker, and performance expert. Over the past decade, he has built a prolific consulting business and continues to work with the best and brightest clients. Providing high-output business success for ambitious, growth-oriented clients is Jake’s passion.
As a result of working with a wide range of clients in a variety of industries for many years, Jake has developed a comprehensive understanding of highly effective business practices. His experience building teams and mentoring leaders has allowed him to learn from each experience and develop unique solutions.
Jake is a strategic consultant who helps organizations reach their full potential and drives success by helping business leaders make calculated and well-informed decisions. Jake has gained a deep understanding of the unique challenges businesses encounter when exploring growth opportunities.
Jake’s experience includes market analysis, financial oversight, profitability assessment, risk management, financial strategy development, operations optimization, and organizational restructuring.
His expertise in implementing emerging blockchain & web3 technologies such as smart contracts, NFTs, DAOs, and the metaverse has given his clients a significant advantage over their competitors.
By leveraging his global network of contacts, Jake can access resources and collaborate across geographies to create long-term value. His clients benefit from customized solutions tailored to their individual needs and personalized guidance throughout the process.
His solutions focus on implementing bespoke scalable business strategies, creating opportunities for expansion into new markets, and identifying the most appropriate exit strategies for businesses to maximize returns.
Get Started Now, Space is Limited
© 2023 Beyond Broke, LLC.


